Molecular Weight Of Nickel Dmg Complex
Posted By admin On 01.12.20| Names | |
|---|---|
| IUPAC name | |
Other names
| |
| Identifiers | |
| |
| ChEMBL | |
| ChemSpider |
|
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.002.201 |
| EC Number | |
PubChemCID | |
| RTECS number |
|
| UNII | |
CompTox Dashboard(EPA) | |
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C4H8N2O2 | |
| Molar mass | 116.120 g·mol−1 |
| Appearance | White/Off White Powder |
| Density | 1.37 g/cm3 |
| Melting point | 240 to 241 °C (464 to 466 °F; 513 to 514 K) |
| Boiling point | decomposes |
| low | |
| Structure | |
| 0 | |
| Hazards | |
| Main hazards | Toxic, Skin/Eye Irritant |
| Safety data sheet | External MSDS |
| GHS pictograms | |
| GHS Signal word | Danger |
| H228, H301 | |
| P210, P240, P241, P264, P270, P280, P301+310, P321, P330, P370+378, P405, P501 | |
| NFPA 704 (fire diamond) | |
| Related compounds | |
| Hydroxylamine salicylaldoxime | |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa). | |
| verify (what is ?) | |
| Infobox references | |
Dimethylglyoxime is a chemical compound described by the formula CH3C(NOH)C(NOH)CH3. Its abbreviation is dmgH2 for neutral form, and dmgH for anionic form, where H stands for hydrogen. This colourless solid is the dioxime derivative of the diketone butane-2,3-dione (also known as diacetyl). DmgH2 is used in the analysis of palladium or nickel. Its coordination complexes are of theoretical interest as models for enzymes and as catalysts. Many related ligands can be prepared from other diketones, e.g. benzil.
Substance Name: Nickel(II) EDTA complex RN: 25481-21-4 InChIKey: HTLPAEWBUABNNS-UHFFFAOYSA-L. Nickel(II) chloride ethylene glycol dimethyl ether complex can be used:. As a catalyst for the borylation of racemic benzylic chloride to synthesize enantioenriched benzylic boronic esters. As a promoter for the trifluoromethylation of alkyl iodides to synthesize broad range of alkyl-CF 3 compounds. If the formula used in calculating molar mass is the molecular formula, the formula weight computed is the molecular weight. The percentage by weight of any atom or group of atoms in a compound can be computed by dividing the total weight of the atom (or group of atoms) in the formula by the formula weight and multiplying by 100. Nickel-dimethylglyoxime complex (abbreviated as Ni(II)(DMG)2) modified carbon paste and graphite electrodes were prepared by mixing Ni(II)(DMG)2 with graphite paste, and coating Ni(II)(DMG)2 to.
However, when following the procedure for Lion you might run into a snag that will prevent the drive from being created. /mac-os-x-lion-installesddmg.html. Additionally, while Apple's OS should be available using Apple's various Internet recovery options, this can often take a long time to download, especially if you do not have the fastest broadband connections available to you.We previously outlined how to when OS X Lion was released, and the process for Mountain Lion is for the most part the same. Purchase and download Lion from the Mac App Store (or use your up-to-date redemption code), and when the download is finished, the Mountain Lion installer will load. Therefore, to create a standalone USB or optical media install drive for OS X 10.8 Mountain Lion, do this:.
Place into an allocated Jewel Socket on the Passive Skill Tree. /is-chaos-dmg-elemental-poe.html.
Molecular Weight Of Nickel Dmg Complex 3
- It may be used in the preparation of nickel dimethylglyoxime, a dye complex used for the fabrication of dye-sensitized solar cells. Dimethylglyoxime may be used as a chelating agent for determining nickel ion in complexes by gravimetric, titrimetric or colorimetric analysis. Packaging 100, 500 g in poly bottle.
- Molecular mass (molecular weight) is the mass of one molecule of a substance and is expressed in the unified atomic mass units (u). (1 u is equal to 1/12 the mass of one atom of carbon-12) Molar mass (molar weight) is the mass of one mole of a substance and is expressed in g/mol. Weights of atoms and isotopes are from NIST article.
- ›› Nickel(II) Sulfate molecular weight. Molar mass of NiSO4 = 154.756 g/mol. When calculating molecular weight of a chemical compound, it tells us how many grams are in one mole of that substance. The formula weight is simply the weight in atomic mass units of all the atoms in a given formula.
Preparation[edit]
Dimethylglyoxime can be prepared from butanone first by reaction with ethyl nitrite to give biacetyl monoxime. The second oxime is installed using sodium hydroxylamine monosulfonate:[1]
Complexes[edit]
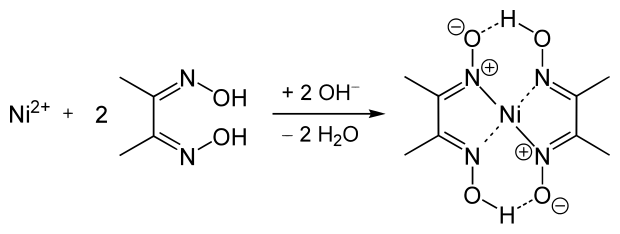

Dimethylglyoxime is used to detect and quantify nickel, which forms the bright red complex nickel bis(dimethylglyoximate) (Ni(dmgH)2). The reaction was discovered by L. A. Chugaev in 1905.[2]
Cobalt complexes have also received much attention. In chloro(pyridine)cobaloxime[3] the macrocycle [dmgH]22− mimics the macrocyclic ligand found in vitamin B12.
References[edit]
Nickel
- ^Semon, W. L.; Damerell, V. R. (1930). 'Dimethylglyoxime'. Organic Syntheses. 10: 22. doi:10.15227/orgsyn.010.0022.CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link)
- ^Lev Tschugaeff (1905). 'Über ein neues, empfindliches Reagens auf Nickel'. Berichte der Deutschen Chemischen Gesellschaft. 38 (3): 2520–2522. doi:10.1002/cber.19050380317.
- ^Girolami, G. S.; Rauchfuss, T.B.; Angelici, R. J. (1999). Synthesis and Technique in Inorganic Chemistry: A Laboratory Manual (3rd ed.). pp. 213–215.
Molecular Weight Of Nickel Dmg Complex 1
| Physical Chemistry Virtual Lab Physical chemistry (also called physicochemistry) is the explanation of macroscopic, microscopic, atomic, subatomic, and particulate phenomena in chemical systems in terms of physical concepts; sometimes using the principles, practices and concepts of physics like thermodynamics, quantum chemistry, statistical mechanics and dynamics. Spectrophotometry Cryoscopy Ebullioscopy EMF measurement Determination of Viscosity of Organic Solvents Adsorption Isotherm Verification of Tafel Equation Determination of Viscosity Average Molecular Weight of Polymer Calorimetry -Water equivalent Calorimetry Calorimetry -Heat of Neutralization |
| Organic Chemistry Virtual Lab Organic chemistry is a discipline within chemistry which involves the scientific study of the structure, properties, composition, reactions, and preparation (by synthesis or by other means) of chemical compounds that contain carbon. Detection of Functional Groups Detection of Elements: Lassaigne鈥檚 Test Separation of Compounds Using Column Chromatography Purification by Fractional distillation/crystallisation Purification by Steam distillation/crystallisation Laser Flash Photometer Organic Preparations - Allylation of Isatin Estimation of Aspirin Estimation Of Glucose Calculation of 位max of Organic Compounds Using Woodward Fieser Rules |
| Inorganic Chemistry Virtual Lab Inorganic chemistry is the branch of chemistry concerned with the properties and behavior of inorganic compounds. This field covers all chemical compounds except the myriad organic compounds (carbon based compounds, usually containing C-H bonds). Water analysis-Determination of Physical parameters Water analysis-Determination of Chemical parameters Acid Base Titration Gravimetric Estimation of Barium Gravimetric Estimation of Nickel Crystal Field Theory Group Theory Alloy Analysis (Brass) Soil Analysis-Determination of Specific conductivity of Soil Soil Analysis-Determination of pH of Soil |
| Advanced Analytical Chemistry Virtual Lab Analytical chemistry is the branch of chemistry concerned with studying the properties of materials and development of tools used to analyze materials. It is the science of sampling, defining, isolating , concentrating and preserving samples. Soil Analysis-Determination of Available Organic Carbon content in the Soil Soil Analysis-Determination of Available Nitrogen content in the Soil by Kjeldahl method Soil Analysis-Determination of Available Phosphorus content in the Soil by Bray's method Electrogravimetric Estimation of Metals Estimation of Phosphate Content in Soft Drinks Flame Photometry Polarography - Determination of Unknown Concentration of Cadmium Polarography - Determination of Unknown Concentration of Vitamin C |